Prioritizing energy efficiency: Digital strategies for operational improvements
Lowering greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to keep global temperatures from rising, but efforts to get the world aligned toward this goal have been inconsistent. For instance, at COP28, the global community set a goal to triple renewable energy capacity and double energy efficiency by 2030 to limit warming to 1.5°C.
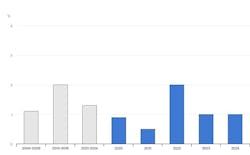
Since then, the rapid scaling of solar, wind and hydro has helped, and much progress has been made toward the target for renewable energy capacity. But, despite its effectiveness, energy efficiency progress has been slow. We’ve only seen a one percent improvement in 2023 and 2024 and a two percent improvement per year between 2010 and 2019 (Figure 1), according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This misses the new target of greater-than four percent improvements per year.
As highlighted by IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol, “Energy efficiency is a key pillar of secure, affordable and inclusive energy transitions.” By shining a spotlight on the industrial sector, one can see the significant impact that energy efficiency improvements could have on global sustainability progress. This important sector accounts for 39 percent of global energy consumption, growing at 1.5 percent per year from 2010 to 2023, according to the IEA. Industrial emissions grew at a slightly slower pace, 1 percent, indicating some improvement in energy intensity.
Overall, progress in this sector has been met with challenges, particularly in hard-to-abate sectors such as chemicals, cement, and steel. This is largely due to the long life of assets and the challenge of developing new technologies and processes, but there are clear paths for improvement.
To circumvent some of these obstacles and take a critical first step, industrial companies are prioritizing energy improvements to current operations. Because their operations are so large and complex, even small efficiency improvements can yield significant benefits both for the environment and business performance. There are many strategies, often powered by digital technologies, companies can pursue to quickly see a positive impact.
The key lies in having the right strategy, data, and digital tools to succeed. Three key areas are taking priority today as crucial to improving energy efficiency across operations, with many examples of how industry leaders are already applying these strategies.
Emissions management
Energy efficiency and emission reduction are inextricably linked. While major emitters have pledged to become more transparent about emission management, many admit they do not know how much they are emitting in real-time and cannot track how operational decisions impact emissions. Fixing a problem that is not adequately measured is difficult, at best.
There are emission management tools available to industrial companies today that can better correlate, analyze, and visualize operational data from across the organization so emission reduction decisions can be made faster, and with more accuracy. By leveling internal silos and revealing real-time data holistically, companies gain better insights into their carbon emissions and abatement, even gaining the ability to create auditable reports that show progress.
A European energy company found success applying an emissions management tool at its refinery in Italy. By combining modeling tools with Industrial AI-based techniques and detailed calculations, the system optimizes economics with total emissions toward achieving more sustainable and profitable operations. With new and increased visibility into its operating and financial data, the company has become more proactive with asset and operating strategies to meet emissions limits. It has also been able to improve its carbon credit management process and assess opportunities to drive sustainability and reduce emissions through feedstock selection and production planning.
AI-driven hybrid models
Industrial processes are inherently complex, making them exceedingly difficult to model for use in AI processes. To augment the process, hybrid models backed by AI can be built using data collected from real assets. They can close the simulation-to-reality gap, resulting in more accurate models that cover more aspects of the operation. Industrial companies can then employ these models to drive increased efficiencies across many of their processes.
For instance, Central Asia producer SOCAR used AI capabilities to boost the efficiency of their acrylonitrile operations, developing a reactor model from operational data and incorporating first principles constraints. The model predicted the percentage of acrylonitrile in reactor flue gases and the optimal pressure required to boost conversion. SOCAR reviewed scenarios to maximize steam generation in the reactor, which helped them improve waste heat recovery by 36 percent and save five percent in fuel gas across the complex.
In another example, global chemical company BASF applied an Industrial AI application to help implement process control capabilities designed to rapidly improve operations at a Gulf Coast site. The AI guidance captured the most difficult and time-consuming elements of implementation, providing guidance for less experienced technical workers to implement a more capable system. A full ROI on this system was achieved in less than six months.
Prescriptive and predictive maintenance
By predicting and preventing equipment failures with early warnings, AI-based asset performance management tools can have a significant impact on reducing energy and emissions. For example, unplanned plant shutdowns often force flaring that can emit as much carbon in a single event as months of normal operations. A proactive and prescriptive approach to asset maintenance with AI-based tools, helps avoid these types of failures, and often yields operational efficiencies in other ways too, such as optimizing spare part inventory, reducing waste, and eliminating time spent on unnecessary, schedule-based maintenance.
Midstream operator OCP Ecuador cut its maintenance costs by 25 percent by employing machine learning capabilities that predict equipment failure and prescribe operational solutions. By analyzing engine and pump performance, the company’s operations teams predicted degradation in advance which enabled them to conduct earlier intervention and resolution. This work also helped the maintenance team improve equipment uptime by 20 percent, while allowing them to significantly improve their spare part management and further reduce their operational costs.
The path forward
Even as macro-environments evolve and countries’ net zero priorities change, industrial companies undoubtedly have a critical role to play in helping us improve energy efficiencies that directly impact global warming. They can make steady gains toward their decarbonization goals by building greater efficiencies into their existing operations, which have proven to not only have a positive impact on the environment but also cost savings and business performance.
1This is a work derived by Paige Morse from IEA material and Paige Morse is solely liable and responsible for this derived work. The derived work is not endorsed by the IEA in any manner.