Most engineers and installers treat thermoplastic piping systems like metal during design and installation. As a result, mechanical stresses get permanently locked into the piping system, which can reduce its life expectancy. This is the most common failure mode of a piping system.
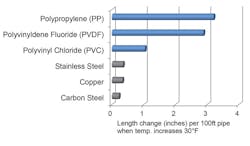
Piping systems are dynamic. They expand and contract due to temperature changes in the ambient environment and the media flowing inside. There may also be a significant temperature difference between time of installation — when the piping gets clamped in place and restrained — and when the system starts operating. Plastics expand and contract at greater rates than metal (see Figure 1). All these factors must be taken into account for proper installation. For example, if a contractor at a food production facility installs a 100-ft straight run of polyvinyldene fluoride (PVDF) pipe on a cool morning (50°F), it will expand 2.88 inches in length when the ambient temperature rises to 80°F.
Figure 1. Thermal expansion: plastic versus metal.
Issues with traditional clamps and supports
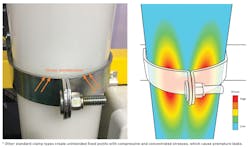
Issues can arise when using traditional pipe and valve support products for plastic piping systems. First, many clamps are designed to hold the pipe firmly or do not prevent an installer from overtightening against the pipe. This can stress the pipe at time of installation and later when it needs to move naturally (see Figure 2). Second, many clamps have sharp metal edges that can easily come in contact with the pipe and cause damage. Third, traditional pipe guides, which do allow movement, do not provide proper pipe support during an earthquake. The pipe can freely move side to side (perpendicular to the axis) and become damaged. This also requires engineers to especially consider the supporting structure beneath the pipe guide because of large forces that would be transferred during an earthquake. Finally, valve manufacturers typically recommend that valves are independently supported in a piping system; in practice, installers often clamp them down as fixed points. The valves then become unintentional fixed points where stresses will concentrate when the pipe cannot move naturally. All of these issues contribute to stress concentrations that increase the risk of premature failures and leaks.
Solution
Improper piping system support can result in premature failures and subsequent damage leading to leaks and expensive downtime for repairs or replacement. New solutions are available to resolve this, such as a pipe and valve support system that has been especially designed to eliminate the stress transfer to pipe due to thermal expansion, installation or seismic events. This system (see Figure 3) includes pipe guides in sizes ½ inch to 8 inches (iron pipe size [IPS] and metric sizes) and valve supports in sizes 3/8 inch to 2 inches. It can be used with any thermoplastic piping system material (PP, PVDF, HDPE, PVC, CPVC, ABS, etc.), as long as it is IPS (inch) or metric size.
Pipe guides
The pipe guides are designed to have a 3-millimeter (mm) gap (oversized) between the plastic insert and the pipe it supports. Molded from low-friction UV-resistant HDPE, the design allows the piping to slide easily and freely in the axial direction with absolute minimal stress and wear during each thermal expansion cycle. An outer metal hoop provides additional strength, but the design of the insert does not allow the pipe to touch the metal hoop. The design also prevents overtightening against the pipe; fastening down the outer metal hoop does not cause the insert to squeeze the pipe.
Figure 2. Stress concentration from traditional pipe
Valve supports
The valve supports (see top photo) allow valves to move in two directions (+/- 3 inches) as the pipe expands and contracts, all in a controlled manner and while properly supported. The support base and slide components are made of low-friction, durable polypropylene (PP). Valves can slide with virtually no resistance. Piping centerlines will be aligned when the pipe guide is mounted one standard strut height taller than the valve support.
Installation
The new pipe guides give installers the flexibility to mount directly on any flat surface, on standard strut, horizontally as a hanger or vertically. In vertical orientation, an elastomer material is inserted to create sufficient friction and snugly secure the pipe. In a horizontal mount, the pipe is free to move. A separate hanger kit allows mounting to all thread or rods connected to the ceiling. In all cases, the pipe never touches the metal hoop or hardware and the design prevents squeezing against the pipe. For easy identification, sizes are embossed and stamped on with IPS inserts in gray and metric inserts in black. The valve support base can be mounted to any flat surface or directly and securely onto standard strut due to the profile molded underside.
Figure 3. The pipe and valve support system from GF Piping Systems includes Stress Less® Pipe Guides and Stress Less® Valve Supports.
Applications
The pipe and valve supports are an engineered solution that can help ensure the entire service life of industrial piping systems. They are recommended for all thermoplastic piping systems, including those in stringent high-purity facilities and in corrosive environments — particularly piping systems in critical applications with aggressive media, indoor-to-outdoor transitions or that are subject to wide temperature variations.
Alphonse Anderson is product manager of Engineered Piping Systems for GF Piping Systems. He holds a master’s degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Michigan and has several years of professional experience in the automotive and oil and gas industries. He may be reached at alphonse. He can be reached at [email protected].