Maintaining optimized hose health with preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance is a must for industrial facilities. Proactive maintenance plans can help operators prevent avoidable downtime and costly replacements by identifying issues before they become major headaches.
But in certain plant applications, it can be challenging to identify the optimal time to replace specific components. Consider industrial hoses, a common component of concern among plant managers around the world. Waiting too long to replace a worn hose can significantly increase the risk of failure. By contrast, replacing a hose prematurely can cost a plant unnecessary time and money. To strike the right balance, plants should implement detailed preventive maintenance plans for industrial hoses that include frequent inspections and proactive replacements. Such plans allow plants to track and optimize hose life spans to save costs.
While tracking the performance of every hose in a plant can take some time, the overall cost-saving benefits make it worth the investment. Imagine a process application using 50 identical hoses in which half are steam cleaned and half are not. The regularly cleaned hoses will tend to wear out after one year of use, while those that are not cleaned will last about five years.
Placing all 50 hoses on the same five-year replacement cycle will be problematic because the steam-cleaned hoses will likely fail unexpectedly, potentially leading to significant downtime and costs, as well as safety concerns. By contrast, a one-year replacement interval for all 50 hoses would also lead to unnecessary costs by replacing 25 hoses that have four years of life remaining. If each hose costs $200, the annual premature replacement of 25 five-year hoses would result in extra expenses of about $20,000 over five years.
To avoid such waste and optimize hose life, here are some tips plant managers can follow to create an effective, preventive hose maintenance plan.
Conduct a hose audit
The ideal replacement interval for any hose largely depends on the environment in which it functions. Operators must consider varying pressure and movement demands on the hose, along with any potential influence from nearby equipment.
Identifying each influential factor for every hose is a good starting point. Conduct a full plant audit, identifying and labeling every hose. Include all important information for each hose, including hose type, process fluid, part number, temperature and pressure ratings, and the contact information for the hose supplier. Also consider color coding hoses to visually distinguish them throughout a plant.
Next, record these details in a spreadsheet, along with the following information:
- Hose length and size
- Core material and construction
- Reinforcement layers
- End connections
- Mounting
- Cover type
- Operating conditions
- Cleaning procedures
- Installation date
Scheduled replacement date
By performing an extensive audit, operators can gain a better understanding of the function and replacement needs of all hoses throughout a plant. A hose supplier can also provide general guidelines for replacements and inspections. Use those recommendations — correlated with each hose’s materials of construction, operating environment and other factors — to gain a better sense of when a particular hose will require attention.
These grab sampling system panels feature elbows and adapters at the horizontal hose end connections to prevent hose strain.
Conduct a hose life cycle analysis
Following an initial audit, begin performing regular visual hose inspections at intervals recommended by the hose supplier. Visual checks do not require system downtime, making them an easy and effective evaluation method.
Look for signs of general deterioration like cuts, scrapes, corrosion, kinks and other signs of wear. These are clear symptoms the hose is ready for replacement. Note them in the spreadsheet and review when the hose was first installed and when inspectors first observed visible deterioration. This time frame provides a clear replacement interval to use for this hose. As a plant determines each hose’s replacement interval, its preventive maintenance plan will begin to take shape, providing an optimized schedule for replacements. However, continue to perform periodic inspections to ensure a change in system parameters has not placed a strain on a hose that will result in a shorter replacement interval.
If a hose has failed despite regular inspection, document every detail available, including the severity of the failure or break, the location of the failed hose and how the hose was mounted. Consult with the hose supplier and share these details to best troubleshoot the cause of the failure.
Prevent excess hose strain
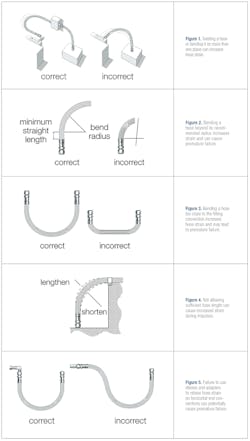
Excess hose strain is one easily preventable cause of premature failure. Hoses that rub against other equipment, are exposed to external heat sources or experience regular pulses are all subject to greater strain. However, most often, excess strain leading to hose failure can be linked to improper hose arrangement. When conducting visual inspections, look for and immediately correct any of the following troublesome arrangements:
- A hose bent beyond its manufacturer-recommended radius (Figure 1)
- A hose that is twisted or bent on more than one plane (Figure 2)
- A hose bent too close to the hose/fitting connection (Figure 3)
- Insufficient hose length, leading to greater strain during impulses (Figure 4)
- Failure of installers to use proper elbows and adapters to relieve hose strain on horizontal end connections (Figure 5)
Determine the need for protective coverings
Many hoses used in industrial environments require supplemental protection to withstand common operating conditions.
Several options exist, depending on where each hose is used. Fire jacketing can provide insulation from internal system fluid temperature extremes. Thermosleeve coverings can protect a hose from weld spatter and resist the effects of UV light. Spiral guard is effective against hose abrasion. Armor guard and spring guard both effectively protect against kinking and abrasion.
When making a selection, remember that no cover will change a hose’s fundamental technical attributes. Also remember to carefully evaluate each option against the desired performance criteria.
Fine-tune maintenance procedures
Once established, a preventive maintenance program can be continuously improved with tweaks over time. Performing destructive testing on a replacement hose, for instance, can help determine whether a hose was replaced too soon or too late. Analyze the recorded historical data to determine if any intervals should be lengthened or shortened. Further, operators can observe which specific hoses require frequent replacement and then consider alternative material options or coverings to prolong the life of those hoses.
Stay prepared with replacement hoses
Once regular replacement intervals have been established, new hoses can and should be ordered in advance. Keeping spare inventory is good practice because even the best preventive maintenance programs cannot predict or prevent every possible issue that may arise.
Spare hoses should typically be on hand for the following circumstances:
- Critical applications. Always keep readily available spares to correct hose applications that present critical safety hazards or severe downtime potential.
- Likely failures. Some hose operating environments simply have greater failure potential. Keep spares on hand to accommodate frequent replacements for hoses kinking, moving in two planes or experiencing vibration, for example. Alternatively, find a more suitable hose for the application or adjust the system to remove strain on the hose.
- Special applications. Keep spares of hoses that present sourcing difficulty. For example, if a hose featuring a specialized material has a three-week lead time from the supplier, keep several spares on hand to avoid prolonged downtime.
Realizing a return on investment
Developing, implementing and maintaining a preventive maintenance plan for industrial hoses requires a significant amount of work, but the investment is worthwhile. With fewer required replacements, enhanced safety and optimized processing uptime, the proof will quickly be revealed in the form of cost savings and improved profitability.
An original version of this article appeared on the Swagelok Reference Point blog here: www.swagelok.com/en/blog/industrial-hose-maintenance-plan-save-plant-thousands.
Alice Chin is field engineer, North America, for Swagelok Company. She can be reached at [email protected].